Some Small & Smart Servers written in Scala, including a nio server and a small httpd, which also supports websocket(v13 only).
It's targeted for small footprint when running, with extensibility for mulit-threading when processing http requests' business.
s-server uses '@sun.misc.Contended' to kick false sharing off, so run it on jvm-8 with -XX:-RestrictContended if asynchronous responses are needed.
Http parsing and rendering are based on spray, but I tweaked it much for performance and code size.
Note that s-server 3.x is the current supported release, other version is deprecated.
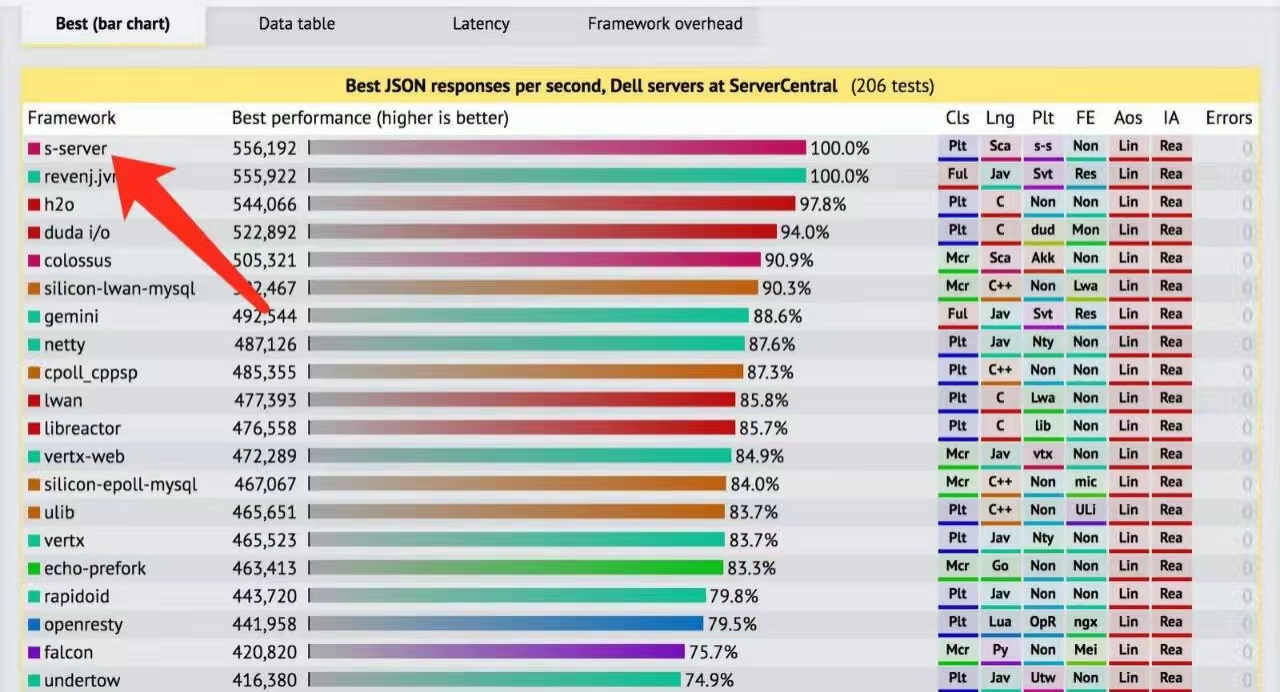
s-server is optimized for tcp services extremely. In TechEmpower Framework Benchmarks (TFB) 2017, s-server got good scores, such as the following:
Three Examples:
-
SampleHttpServer
This sample http server contains synchronous response only.
To request using pipelining, just run'nc -C 127.0.0.1 8787 < src/test/scala/woshilaiceshide/sserver/http-requests.dos.txt'. -
AdvancedHttpServer
This sample http server contains synchronous response, asynchronous response, chunked response, response for chunked request, websocket, and is enabled with pipelining.
To request using pipelining, just run'nc -C 127.0.0.1 8787 < src/test/scala/woshilaiceshide/sserver/http-requests.dos.txt'.
To test the above examples, just type the following command in your sbt console:
-
type
'test:run'in your sbt console to run'woshilaiceshide.sserver.test.EchoServer' -
type
'test:runMain'in your sbt console followed by a'TAB'to prompt you the valid choices -
type the following commands in your sbt console to make a standalone distribution with all the tests using sbt-native-packager:
set unmanagedSourceDirectories in Compile := (unmanagedSourceDirectories in Compile).value ++ (unmanagedSourceDirectories in Test).value
set mainClass in Compile := Some("woshilaiceshide.sserver.test.EchoServer")
#or set mainClass in Compile := Some("woshilaiceshide.sserver.test.SampleHttpServer")
#or set mainClass in Compile := Some("woshilaiceshide.sserver.test.AdvancedHttpServer")
stage
If proxy is needed:
sbt \
-Dsbt.repository.config=./repositories \
-Dsbt.override.build.repos=true \
-Dhttp.proxyHost=${proxy_host} -Dhttp.proxyPort=${proxy_port} -Dhttp.proxyUser=${proxy_user} -Dhttp.proxyPassword=${proxy_password} \
-Dhttp.nonProxyHosts="localhost|127.0.0.1" \
-Dhttps.proxyHost=${proxy_host} -Dhttps.proxyPort=${proxy_port} -Dhttps.proxyUser=${proxy_user} -Dhttps.proxyPassword=${proxy_password} \
-Dhttps.nonProxyHosts="localhost|127.0.0.1" \
-Dsbt.gigahorse=false \
-v -d stageIf no proxy is needed:
sbt -Dsbt.repository.config=./repositories -Dsbt.override.build.repos=true -v -d stage- small footprint when running. HOW SMALL? Try by yourself, and you'll get it!
- only one single thread is needed for basic running, and this thread can be used as an external task runner and a fuzzy scheduler. (the builtin fuzzy scheduler may be disabled when constructing the server instance.)
- support multi-threading when processing messages in business codes
- builtin checking for idle connections
- builtin support for throttling messages
- support http pipelining
- support http chunking
- support websocket(v13 only)
- plain http connections can be switched(upgraded) to websocket connections. (but not vice versus)
The previous releases(<= v2.5) of s-server have dealt with 100% CPU with epoll. The main related codes can be seen on this link. Since 3.x, s-server clears out all those codes. So do not run s-server on jdk 6 and 7.
- requests flow in
channel - and handled by
channel handler - and
channel handlermay usechannel wrapperto write responses.
-
I've published s-server to bintray, you can add the following line in your build.sbt:
resolvers += "Woshilaiceshide Releases" at "http://dl.bintray.com/woshilaiceshide/maven/"
libraryDependencies += "woshilaiceshide" %% "s-server" % "3.1" withSources()
-
build s-server locally using
'sbt publishLocal'.
- I'v written a project named Scala-Web-REPL, which uses a web terminal as its interactive console.
- ... If your development touches
's-server', you may tell me to write your project here.
- optimize socket i/o operations: 1). reducing i/o operations, 2). making i/o just carried out as directly as possible without repost them to the underlying executor.
- optimize the http parsing processes. Spray's http parser is not good enough, and some tweaks are needed.
- reuse more objects no matter what footprints they occupy, especially for i/o, parsing, rendering.
- write test cases
- ...
- use jol to inspect MEMORY
- use jitwatch about BYTE CODE & JIT, see https://medium.com/@malith.jayasinghe/performance-improvements-via-jit-optimization-aa9766b705d2
- use alibaba arthas for introspection & trace & diagnostic
When the input stream is shutdown by the client, the server will read "-1" bytes from the stream. But, "-1" can not determine among "the entire socket is broken" or "just the input is shutdown by peer, but the output is still alive".
I tried much, but did not catch it!
Business codes may "ping" to find out weather the peer is fine, or just shutdown the whole socket in this situation. The key hook is "woshilaiceshide.sserver.nio.ChannelHandler.inputEnded(channelWrapper: NioSocketServer.ChannelWrapper)". In most situations, You can just close the connection